
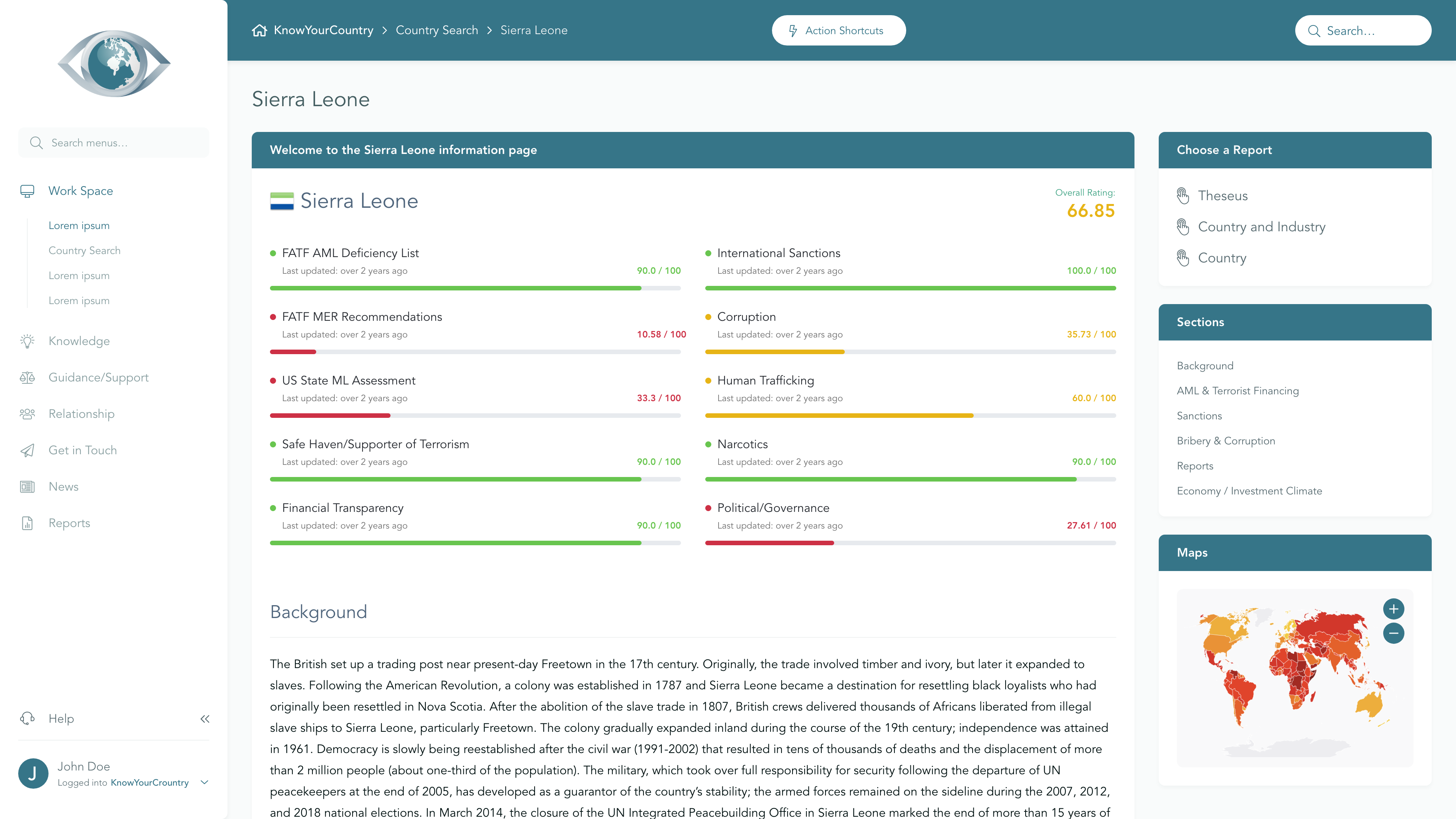
Libya Country Summary
Higher Risk
View full Ratings TableSanctions
Higher Concern
FATF AML Deficient List
Medium Concern
Terrorism
Medium Concern
Corruption
Higher Concern
US State ML Assessment
Lower Concern
Criminal Markets (GI Index)
Higher Concern
EU Tax Blacklist
Lower Concern
Offshore Finance Center
Lower Concern
Please note that although the below Summary will give a general outline of the AML risks associated with the jurisdiction, if you are a Regulated entity then you may need to demonstrate that your Jurisdictional AML risk assessment has included a full assessment of the risk elements that have been identified as underpinning overall Country AML risk. To satisfy these requirements, we would recommend that you use our Subscription area.
If you would like a demo of our Subscription area, please reserve a day/time that suits you best using this link, or you may Contact Us for further information.
Anti Money Laundering
FATF Status
Libya is not on the FATF List of Countries that have been identified as having strategic AML deficiencies
Compliance with FATF Recommendations
Libya has not yet undertaken a Mutual Evaluation Report relating to the implementation of anti-money laundering and counter-terrorist financing standards.
Sanctions
A broad, multilayered set of sanctions is enforced against Libya by the United Nations and multiple national actors, including the United States (OFAC), the European Union, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, Japan, New Zealand, and Switzerland, covering arms embargoes, asset freezes (notably on the Libyan Investment Authority), travel bans, and restrictions on illicit petroleum exports. These measures are complemented by maritime enforcement and various sectoral restrictions—such as oil trade controls and financial prohibitions—with enforcement instruments like EU Operation IRINI and national licensing regimes illustrating how different jurisdictions implement and police the sanctions.
Criminality
Rating |
0 (bad) - 100 (good) |
|---|---|
| Transparency International Corruption Index | 13 |
| World Bank: Control of Corruption Percentile Rank | 4 |
Libya is grappling with pervasive corruption and a range of criminal activities, including human trafficking, arms smuggling, and financial crimes, which are exacerbated by weak governance and ineffective law enforcement. The country's political instability and reliance on militias hinder efforts to combat organized crime, while the judicial system remains fragmented and under-resourced, leaving civil society and victims of crime with limited support and protection.
Economy
Libya presents a complex investment climate characterized by significant potential due to its abundant natural resources and reconstruction needs, yet it remains hindered by a challenging regulatory environment and political instability. The Government of National Unity (GNU), established in 2021, aims to attract foreign investment, but obstacles such as bureaucratic opacity, corruption, and armed group threats continue to deter investors. While Libya's oil and gas sectors dominate its economy, accounting for the vast majority of government revenue, the lack of a unified political framework and compliance with contractual obligations further complicates the investment landscape, making it imperative for potential investors to navigate these risks carefully.
Subscribe to
Professional Plus
- Unlimited Access to full Risk Reports
- Full Dataset Download
- API Access
- Virtual Asset Risk Assessments

